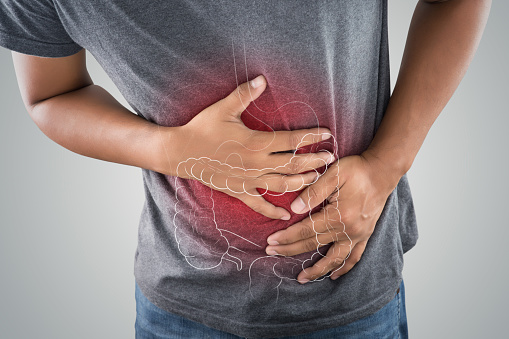
Today in this article, we will be talking about abdominal pain. Abdominal Pain is a topic of great concern among people. No one really wants pain of any sort. In particular, abdominal pains are many a times too excruciating and troublesome.
Table of Contents
- What is abdominal pain?
- Why does abdominal pain occur?
- How to reduce abdominal pain?
- Do I require any kind of investigation?
- What are the home remedies against abdominal pain?
- Abdominal Pain: Types and Home Treatment
- Types of Abdominal Pain
- Causes of Abdominal pain
- How to keep a watch on Abdominal Pain?
- Home treatments
- How to improve on various habits?
- What does the gastrointestinal system include?
- Gastric observations in COVID-19 patients
- COVID 19 and respiratory concerns
- Conclusion
What is abdominal pain?
Before understanding what abdominal pain is, we will first see what the abdomen is. The abdomen is that portion of the human body, right from the diaphragm on the top, at the level of the ribs and going all the way down to the pelvic girdle. The diaphragm, which is in fact a big muscle, separates the chest cavity from the abdomen and as we go downwards, the pubic symphysis forms the front edge of the bony cover of the lower part of the abdomen that goes all the way back to the sacrum bone of the pelvic girdle.
As many of us might know, the abdomen consists of various organs such as the stomach, small intestine and the large intestine. It also houses the liver with the gallbladder, pancreas and the spleen. It then goes down towards the large intestine followed by the rectum, which finally opens into the anal canal. The abdomen also houses the kidneys and the female reproductive organs – uterus and the ovaries. In males, the abdomen houses various glands and ultimately continues into the pelvic girdle. Thus a number of organs lead to abdominal pain.
Why does abdominal pain occur?
Any pain occurs when there is something disagreeable to the body. Or something that causes swelling redness, formation of a tumour or heat to the body parts. For abdominal pain, the major cause is intake of indigestible food. It could be due to infection in the stomach, intestine, kidneys and the other small organs located in the abdomen. All these pains have one thing in common; there is an obstruction or there is an infection. For example, there could be an obstruction in the gallbladder situated in the liver leading to reduced secretion of bile juice. Even in the kidneys, there could be an obstruction due to kidney stones. Sometimes, long-term constipation, which results in hardened stool in the intestine, can also lead to pain in the abdomen.
How to reduce abdominal pain?
Abdominal pain can be reduced either by removing the obstruction or by removing the infection in the organ. Address these two major issues, and the pain subsides rather quickly. With time, the swelling and discomfort also reduces. Antibiotics help reduce pain due to infection. Antibiotics are present in modern medicines, Ayurveda or Homoeopathy,. They are given as necessary to reduce inflammation or swelling in the organs.
What are the different kinds of medicines that may be helpful?
As of now, there are hundreds of kinds of medicines, which can be helpful in reducing abdominal pain. Your doctor is the right person to decide which kind of medicine will suit you best. It depends upon the severity of the pain and the molecules of medicines that would be easily available.
Do I require any kind of investigation?
At times, diagnosing abdominal pain may require certain investigations to be carried out. One of the most popular forms of investigation of the abdomen is Ultrasound Sonography. Through this investigative procedure, the various organs and the structures are seen and analysed by a Radiologist. Depending upon the kind of swelling, infection, inflammation or obstruction, Ultrasound Sonography shows the concerned organs in good detail.
Alternatively, an Endoscopy or a rectoscopy can be done. Here a camera with a light source in front of the equipment takes pictures of the insides of the rectum, large intestine, small intestine and the stomach. This helps in understanding if there are any irritations, inflammations, infections, ulcers or even polyps that may be growing inside and causing the pain.
Some of the other investigative techniques include X Rays, MRI scan, CT scan and sometimes even biopsy.
What are the home remedies against abdominal pain?
Abdominal pain is largely caused due to increased acid secretion in the stomach or increased bile secretions in the intestine. If either of these secretions crosses into other areas, like bile excessively reaching into the stomach or high levels of acid coming into the intestines, they can cause irritation and pain. In such circumstances, the pain can also be controlled by taking some home remedies.
Home remedies come in a lot of variations. Some of the popular ones being Aloe vera drink, water with Apple Cider Vinegar or water with baking soda, which helps reduce the irritation in the stomach. One may also like to use Aloe vera with Apple Cider Vinegar and turmeric. Even a simple preparation of water with fennel and cumin seeds proves to be very useful as a home remedy.
Abdominal Pain: Types and Home Treatment

Next, we will discuss the different types of Abdominal pain. The treatment path we may follow will depend entirely on the kind of pain we experience.
Types of Abdominal Pain
Pain could be of various types – Acute Pain, Chronic Pain and Progressive Pain.
- Acute pains are those, which last only for a few hours or at the most a day or two.
- Chronic pains are the ones that last for a long time. The duration of which could be in weeks or even months.
- The above two types of pains may come and go. However, the third category of pain, the progressive abdominal pain. It hangs on and keeps getting worse over a period of time. To make things worse, it also comes with a few other symptoms as well.
Causes of Abdominal pain
Whether the pain is small, mild or severe, there could be different reasons for it. One of the major reasons for abdominal pain is hard stools, which is mostly due to constipation. Indigestion and viral or bacterial infection could also lead to abdominal pain. Some women experience pain during the menstrual period. Some of the other reasons for the pain are:
- Gas formation in the digestive tract
- Allergies
- Food poisoning
- Ulcers
- Urinary tract infection
- Strain on abdominal muscle and so on.
Sometimes constipation may make it difficult to pass gas and even that could lead to abdominal pain.
In recent years, some people intolerant to lactose or gluten. They are getting ulcers that lead to pain and belly cramps. Conditions such as Pelvic Inflammatory Diseases (PID) may also lead to pain in women. Abdominal pain also arises due to:
- Gallstones
- Kidney stones
- Endometriosis in women
- Inflammation of the appendix
- Diverticulitis
- Blockage in the bowels and
- Loop formation of the bowels.
One of the rare causes is cancer in one or more organs of the abdomen. Interestingly, reduced blood flow or anaemic condition could also lead to pain in the abdomen.
How to keep a watch on Abdominal Pain?
In abdominal pain, there are few symptoms, which occur concomitantly. These are very important for your doctor to understand. So look out for symptoms such as:
- Fever
- Dehydration
- The urge for frequent urination
- Change in colour of urine
- Change in bowel movements
- Nausea or
- Vomiting
Inform your doctor immediately if you observe:
- Tenderness of the belly
- Have been vomiting
- Notice blood or black colour stool.
Also, keep a watch on your eyes. If they turn yellow, or your skin turns pale, or if you find you are pregnant, doctors will approach then a different treatment path.
Home treatments
- Medications using Apple Cider Vinegar or Ayurvedic tablets like Sanjivani can at times be very effective.
- Look into using fennel and cumin seeds.
- Reduce excess intake of coffee and alcohol.
- If you are a smoker, you may think of quitting smoking.
- Perform investigations as per doctor’s prescription.
How to improve on various habits?
As a conclusion for better health, eat smaller portions of food at greater intervals of time. Most importantly, eat slowly and chew the food well. Do not just simply swallow or chew partially. If chewed well, it becomes easy for our digestive system to work. Make sure to not drink fluids that are excessively hot or cold; your intestines might not function optimally, otherwise. Whenever subjected to stress, take measures to reduce it. At all times, whether sitting, standing or walking, we should maintain a good posture and get into physical activities on a regular basis.

Next, we will discuss the presence of Abdominal Pain and its relation with the current coronavirus caused COVID-19 pandemic. As we have understood until now, since the last one and a half year or more, the coronavirus has majorly wrecked havoc with the respiratory system. People suffering from COVID-19 experience some kind of stomach or intestine related ailments and symptoms too. Of late, the percentage of gastrointestinal tract illnesses are on the rise. With COVID-19, the risk of disease in the gastrointestinal tract and their severity are increasing multi-fold.
What does the gastrointestinal system include?
The gastrointestinal system basically includes:
- Mouth
- Food tube (also called the oesophagus)
- Stomach
- Small intestine
- Large intestine and
- The anal tract.
Some of the symptoms shown by people suffering from ailments in the gastrointestinal system are:
- Nausea
- Abdominal pain
- Cramps
- Vomiting and
- Loose bowels
According to ‘Medical News Today’ article, in the US alone, around 40% of patients suffering from COVID-19 have diarrhea, nausea and loss of appetite. However, the lack of appetite is the most common symptom in people suffering from COVID-19 and also after recovery.
Gastric observations in COVID-19 patients
Apart from the above, other gastric observations made in COVID-19 patients include lack of smell, taste and loose bowels. Abdominal pain during COVID-19 is also accompanied by:
- Belching
- Intestinal inflammation
- Acid reflux and
- Occasional bleeding in the stomach or intestines.
COVID 19, as a result, affects the function of intestines and bowels, which in turn takes a lot of time to recover. On certain rare occasions, COVID-19 positive people experience only abdominal pain and no respiratory illnesses or fever.
COVID 19 and respiratory concerns
Some researchers found that stomach and intestine ailments occurring in earlier stages of COVID-19 infection complicating to respiratory concerns. So conclusively, what we can say is that the SARS-CoV-2 causes infections in different parts of the body. It is not that the respiratory system alone is vulnerable to the virus attack. The abdominal organs, gastrointestinal tracts and various other areas are prone to attack as well. Microscopic studies have shown the SARS-CoV-2 virus entering into the intestinal cells. The entry has been seen through the ACE2 protein receptor and finally getting embedded into the cells. The virus starts producing its own copies after it has bound with the cell. This is how the different body organs get infected and the coronavirus colonies continue to grow in the body.
Conclusion
Those people who have their intestines infected suffer from abdominal pain, nausea and diarrhea. The disturbed micro gut flora, also called the gut microbiota, may take quite a while to improve. This article thus helps you be aware of the causes of abdominal pain and in understanding how the coronavirus could be responsible for many of these pains. Knowing these details will help you make an informed decision when affected by both COVID-19 and abdominal pain. It also helps your family physician in diagnosing your illness much more accurately and thus help you recover quickly. Check out our article on Lifestyle disorders to know more about other diseases bringing Abdominal Pain.









One thought on “What is Abdominal Pain and how to treat it”
Comments are closed.