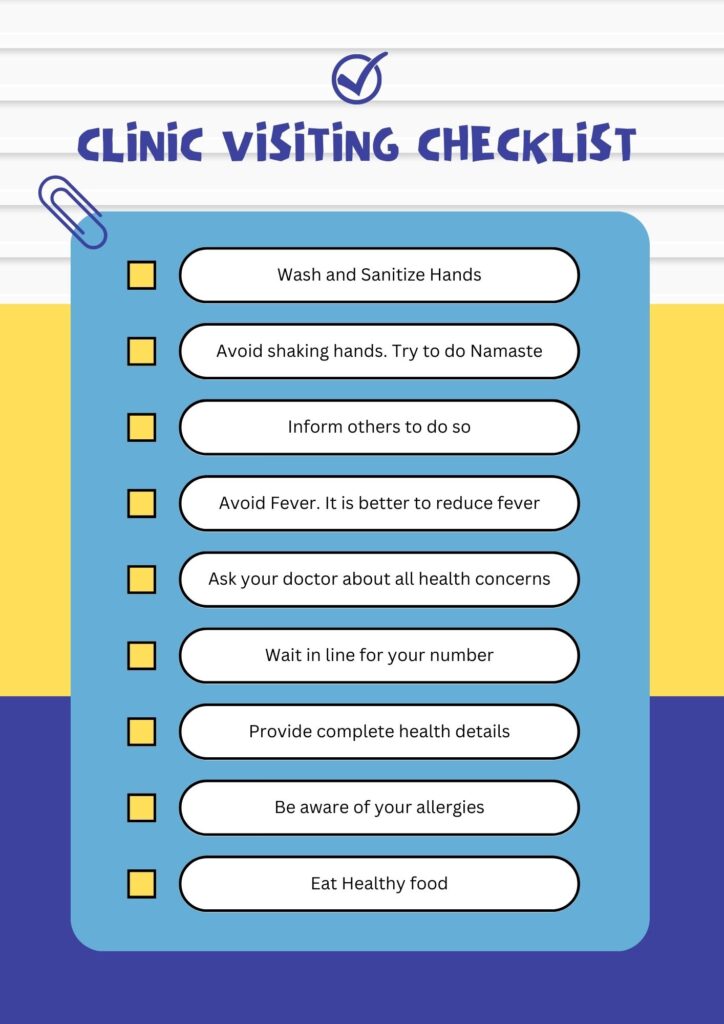
After Henle’s loop, we have the distal tubule, which is quite thick in nature compared to the proximal tubule. Absorption of sodium chloride is quite low over here and water reabsorption may be variable. Like, if there is an excess amount of water to be reabsorbed then that is reabsorbed, otherwise, most of it goes to the collecting tubule, which is the next part of the nephrons.
The urine will be in diluted form if the intake of water is more and of a thicker consistency if intake is less. It is at this place that the diuretic class of modern medicines work and help increase or decrease the flow of urine. All this is made possible by proteins called aquaporins, which work on the distal tubule or distal convoluted tubule part of the nephrons. Sodium chloride continues to be reabsorbed from the lumen of the tube and it works more due to the functioning of the aldosterone.
In the next article, we talk about the collecting tubules and ducts of the nephrons.